Pathobiology
Spondyloarthritis pathobiology is complex
There are many clinically validated targets involved in spondyloarthritis pathobiology, including IL-17, TNF, IL-12, IL-23 and JAK/STAT. Here, we focus on extracellular cytokine targets IL-17, TNF, IL-12 and IL-23.¹
Watch Prof Sewerin decipher the role of extracellular cytokine targets in SpA pathobiology by playing the animation below
There are many clinically validated targets involved in spondyloarthritis pathobiology, including IL-17, TNF, IL-12, IL-23 and JAK/STAT. Although the relative contributions of each are complex, important distinctions are emerging about which cytokines contribute to the various clinical manifestations and SpA disease phenotypes.2,3,9,10,11 Emerging studies are revealing a new dimension of complexity in the IL-17 pathway that may help explain its in vivo functions.12
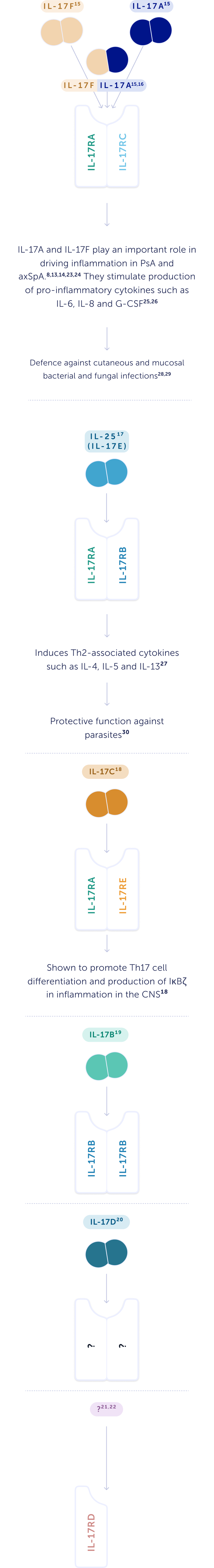
What is the role of the different cytokines in the IL-17 family?
Whilst different in structure, IL-17A and IL-17F have a very similar biological function.13 IL-17A and IL-17F combine to form homo- and heterodimers.14
Speak with a member of our medical team.
If you have questions or want to know more, please reach out to our medical team.
- 1
- McGonagle DG et al. Front Immunol. 2021;12:614255.
- 2
- McGonagle DG et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(9):1167–1178.
- 3
- Rosine N, Miceli-Richard C. Front Immunol. 2021;11:553742.
- 4
- Tsukazaki H, Kaito T. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(17):6401.
- 5
- Cole S et al. Front Immunol. 2020;11:585134.
- 6
- Blanco P et al. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008;19(1):41–52.
- 7
- Russell T et al. Cells. 2021;10(2):341.
- 8
- Glatt S et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:523–532.
- 9
- Rezaiemanesh A et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;100:198–204.
- 10
- Hammitzsch A et al. Front Immunol. 2020;11:591176.
- 11
- Siebert S et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(8):1015–1018.
- 12
- Li X et al. Nat Immunol. 2019;20(12):1594–1602.
- 13
- Yang XO et al. J Exp Med. 2008;205(5):1063–1075.
- 14
- Goepfert A et al. Immunity. 2020;52(3):499–512.
- 15
- Toy D et al. J Immunol. 2006;177(1):36–39.
- 16
- Wright JF et al. J Immunol. 2008;181(4):2799–2805.
- 17
- Rickel EA et al. J Immunol. 2008;181:4299–4310.
- 18
- Chang SH et al. Immunity. 2011;35(4):611–621.
- 19
- Shi Y et al. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(25):19167–19176.
- 20
- Starnes T et al. J Immunol. 2002;169(2):642–646.
- 21
- Yang RB et al. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(35):33232–33238.
- 22
- Monin L et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018;10(4)a028522.
- 23
- Jadon DR et al. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(11):609–627.
- 24
- Shah M et al. RMD Open. 2020;6(2):e001306.
- 25
- Fossiez F et al. J Exp Med. 1996;183:2593–2603.
- 26
- Hymowitz SG et al. EMBO J. 2001;20(19):5332–5341.
- 27
- Fort MM et al. Immunity. 2001;15:985–995.
- 28
- Puel A et al. Curr Opin Immunol. 2010;22(4):467–474.
- 29
- Ishigame H et al. Immunity. 2009;30(1):108–119.
- 30
- Owyang AM et al. J Exp Med. 2006;203(4):843–849.
- APC
- antigen-presenting cell
- axSpA
- axial spondyloarthritis
- CCL
- C-C motif chemokine ligand
- CNS
- central nervous system
- G-CSF
- granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
- IL
- interleukin
- ILC
- innate lymphoid cell
- JAK
- Janus kinase
- MAIT
- mucosal-associated invariant T cell
- PsA
- psoriatic arthritis
- STAT
- signal transducer and activator of transcription
- Th
- T helper cell
- TNF
- tumour necrosis factor